
INSIGHT NOV 26, 2024
The Science of Environmental Comfort: Integrating Comfort with Sustainability in Modern Architecture and Urban Planning
In the contemporary realm of architecture and urban planning, the concept of environmental comfort transcends mere temperature control, embodying a holistic approach that harmonizes human well-being with ecological sustainability. As we delve deeper into the 21st century, the significance of environmental comfort in designing living and working spaces is increasingly recognized, not only for its impact on occupants' health and productivity but also for its role in promoting sustainable practices. This comprehensive discussion aims to unpack the science of environmental comfort, highlighting its critical importance and the innovative strategies employed to achieve it in modern architecture and urban planning.
Understanding Environmental Comfort
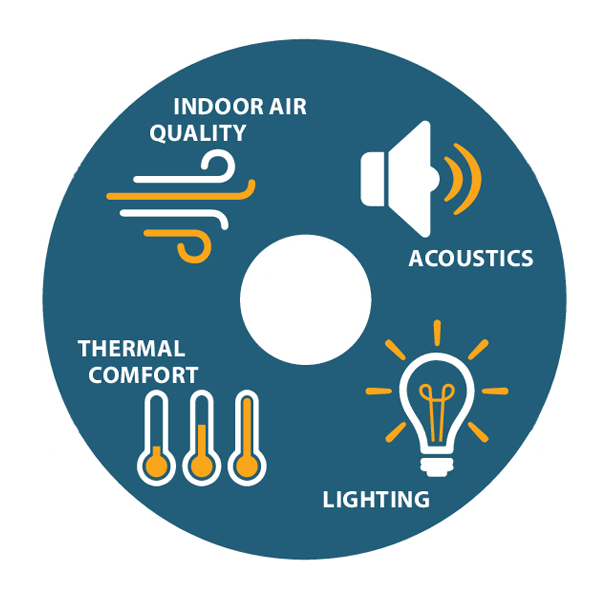
Environmental comfort is a multidimensional concept that encompasses various aspects of the human experience within built environments, including thermal comfort, acoustic comfort, visual comfort, and indoor air quality. Achieving environmental comfort involves creating conditions that naturally meet the physiological and psychological needs of occupants, enhancing their satisfaction and performance while minimizing the environmental footprint of buildings and urban spaces.
Thermal Comfort
Thermal comfort refers to the condition of mind that expresses satisfaction with the thermal environment. It is influenced by numerous factors, including air temperature, humidity, airflow, and the thermal properties of clothing and activity levels. Modern architecture seeks to achieve thermal comfort through energy-efficient heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, passive solar design, and materials that regulate indoor temperatures.
Acoustic Comfort
Acoustic comfort involves the management of sound levels to prevent noise pollution and enhance the auditory experience within a space. This can be achieved through the use of sound-absorbing materials, the strategic placement of buildings and landscaping to shield against external noise, and the design of interior spaces to minimize echo and reverberation.
Visual Comfort
Visual comfort is concerned with ensuring adequate and comfortable lighting levels, minimizing glare, and providing access to natural light. Strategies to achieve visual comfort include the use of daylighting techniques, intelligent lighting systems that adjust to natural light availability, and the careful selection of artificial lighting fixtures that mimic the spectrum of natural light.
Indoor Air Quality
Indoor air quality is a critical component of environmental comfort, referring to the cleanliness of the air within and around buildings. Enhancing indoor air quality involves controlling sources of pollution, ensuring adequate ventilation, and incorporating air purification systems to remove contaminants from the air.
Indoor Environmental Quality Parameters @Medium
The Holistic Approach to Environmental Comfort
Achieving environmental comfort in modern architecture and urban planning requires a holistic approach that considers the interplay between various comfort factors and sustainability. This approach integrates passive design principles, renewable energy sources, and innovative technologies to create environments that are comfortable, healthful, and environmentally friendly.
Passive Design Principles
Passive design utilizes the natural movements of heat and air to maintain comfortable indoor conditions without the need for mechanical systems. Techniques such as orientation for optimal solar gain, thermal mass for heat storage, and natural ventilation are key to passive design, reducing reliance on energy-intensive HVAC systems.
Renewable Energy and Sustainable Technologies
Incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, alongside sustainable technologies like green roofs and rainwater harvesting systems, contributes to environmental comfort while promoting sustainability. These technologies not only support the energy efficiency of buildings but also enhance the overall quality of the urban environment.
The Role of Green Spaces
Green spaces within urban environments play a vital role in enhancing environmental comfort by providing shade, cooling urban heat islands, and improving air quality. The integration of parks, gardens, and green corridors into urban planning is essential for creating comfortable and sustainable urban spaces.

The concept of clean and sustainable development @vecteezy
Addressing the Challenges of Environmental Comfort
Achieving environmental comfort in the face of climate change and urbanization presents significant challenges. These include balancing the increasing demand for comfortable living and working spaces with the need to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Innovations in material science, building technology, and urban design, along with a commitment to sustainable practices, are key to overcoming these challenges.
Conclusion: Pioneering Comfort and Sustainability
The pursuit of environmental comfort in modern architecture and urban planning represents a pivotal step towards a sustainable future. By adopting a holistic approach that integrates comfort with sustainability, architects and urban planners can create spaces that not only cater to the well-being of occupants but also contribute positively to the environment. In this journey, innovation, research, and a collective commitment to sustainability are paramount.
How ECOBUILD Can Help?
At ECOBUILD, we specialize in the integration of environmental comfort and sustainability in modern architecture and urban planning. Our expertise encompasses innovative design solutions, energy-efficient technologies, and sustainable practices that enhance the comfort and well-being of occupants while minimizing the environmental impact. Let ECOBUILD assist you in crafting spaces that are not only comfortable and sustainable but also tailored to the needs of the future.
